给定两个数组 nums1 和 nums2 ,返回 它们的交集 。输出结果中的每个元素一定是 唯一 的。我们可以 不考虑输出结果的顺序 。
1 2 输入:nums1 = [1,2,2,1], nums2 = [2,2] 输出:[2]
思路1:集合 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 class Solution { public int [] intersection(int [] nums1, int [] nums2) { Set<Integer> set1 = new HashSet <Integer>(); Set<Integer> set2 = new HashSet <Integer>(); for (int num : nums1){ set1.add(num); } for (int num: nums2){ set2.add(num); } return getIntersection(set1,set2); } public int [] getIntersection(Set<Integer> set1,Set<Integer> set2){ if (set1.size() > set2.size()){ return getIntersection(set2,set1); } Set<Integer> intersectionSet = new HashSet <Integer>(); for (int num : set1){ if (set2.contains(num)){ intersectionSet.add(num); } } int [] intersection = new int [intersectionSet.size()]; int index = 0 ; for (int num : intersectionSet){ intersection[index++] = num; } return intersection; } }
时间复杂度:O(m+n)
空间复杂度:O(m+n)
思路2:排序+双指针 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution { public int [] intersection(int [] nums1, int [] nums2) { Arrays.sort(nums1); Arrays.sort(nums2); int length1 = nums1.length, length2 = nums2.length; int [] intersection = new int [length1 + length2]; int index = 0 , index1 = 0 , index2 = 0 ; while (index1 < length1 && index2 < length2) { int num1 = nums1[index1], num2 = nums2[index2]; if (num1 == num2) { if (index == 0 || num1 != intersection[index - 1 ]) { intersection[index++] = num1; } index1++; index2++; } else if (num1 < num2) { index1++; } else { index2++; } } return Arrays.copyOfRange(intersection, 0 , index); } }
时间复杂度:O(mlogm+nlogn)
空间复杂度:O(logm+logn)
给你一个字符串 s ,请你去除字符串中重复的字母,使得每个字母只出现一次。需保证 返回结果的字典序最小 (要求不能打乱其他字符的相对位置)
1 2 3 4 5 输入:s = "bcabc" 输出:"abc" 输入:s = "cbacdcbc" 输出:"acdb"
思路:贪心+单调栈 详细视频讲解
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 class Solution { public String removeDuplicateLetters (String s) { int len = s.length(); char [] charArray = s.toCharArray(); int [] lastIndex = new int [26 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i < len ; i++){ lastIndex[s.charAt(i)-'a' ] = i ; } Deque<Character> stack = new ArrayDeque <>(); boolean [] visited = new boolean [26 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i < len ; i++){ if (visited[s.charAt(i) - 'a' ]){ continue ; } while (!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peekLast() > charArray[i] && lastIndex[stack.peekLast() - 'a' ]>i){ Character top = stack.removeLast(); visited[top - 'a' ] = false ; } stack.addLast(charArray[i]); visited[charArray[i] - 'a' ] = true ; } StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder (); for (char c : stack){ stringBuilder.append(c); } return stringBuilder.toString(); } }
给你一个字符数组 chars ,请使用下述算法压缩:
从一个空字符串 s 开始。对于 chars 中的每组 连续重复字符 :
如果这一组长度为 1 ,则将字符追加到 s 中。
请在 修改完输入数组后 ,返回该数组的新长度。
你必须设计并实现一个只使用常量额外空间的算法来解决此问题。
1 2 3 输入:chars = ["a","a","b","b","c","c","c"] 输出:返回 6 ,输入数组的前 6 个字符应该是:["a","2","b","2","c","3"] 解释:"aa" 被 "a2" 替代。"bb" 被 "b2" 替代。"ccc" 被 "c3" 替代。
思路:双指针 为了实现原地压缩,我们可以使用双指针分别标志我们在字符串中读和写的位置。每次当读指针read 移动到某一段连续相同子串的最右侧,我们就在写指针write处依次写入该子串对应的字符和子串长度即可。
在实际代码中,当读指针read 位于字符串的末尾,或读指针 read 指向的字符不同于下一个字符时,我们就认为读指针 read 位于某一段连续相同子串的最右侧。该子串对应的字符即为读指针 read 指向的字符串。我们使用变量 left 记录该子串的最左侧的位置,这样子串长度即为 read−left+1。
特别地,为了达到 O(1) 空间复杂度,我们需要自行实现将数字转化为字符串写入到原字符串的功能。这里我们采用短除法将子串长度倒序写入原字符串中,然后再将其反转即可。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 class Solution { public int compress (char [] chars) { int n = chars.length; int left = 0 ,write = 0 ; for (int read = 0 ; read < n ; read++){ if (read == n-1 || chars[read] != chars[read+1 ]){ chars[write++] = chars[read]; int num = read - left + 1 ; if (num > 1 ){ int anchor = write; while (num > 0 ){ chars[write++] = (char )(num%10 + '0' ); num /= 10 ; } reverse(chars,anchor,write-1 ); } left = read+1 ; } } return write; } public void reverse (char [] chars,int left,int right) { if (left < right){ char temp = chars[left]; chars[left] = chars[right]; chars[right] = temp; left++; right--; } } }
给你一个二进制数组 nums ,你需要从中删掉一个元素。
请你在删掉元素的结果数组中,返回最长的且只包含 1 的非空子数组的长度。
如果不存在这样的子数组,请返回 0 。
1 2 3 输入:nums = [1,1,0,1] 输出:3 解释:删掉位置 2 的数后,[1,1,1] 包含 3 个 1 。
思路:递推优化 在删掉元素的结果数组中,最长的且只包含 1 的非空子数组存在两种情况:
这个子数组在原数组中本身就是连续的,无论删或者不删其他的元素,它都是最长的且只包含 1 的非空子数组;
这个子数组原本不连续,而是两个连续的全 1 子数组,中间夹着一个 0,把这个 0 删掉以后,左右两个子数组组合成一个最长的且只包含 1的非空子数组。
详细题解
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution { public int longestSubarray (int [] nums) { int ans = 0 ; int p0 = 0 , p1 = 0 ; for (int num : nums) { if (num == 0 ) { p1 = p0; p0 = 0 ; } else { ++p0; ++p1; } ans = Math.max(ans, p1); } if (ans == nums.length) { --ans; } return ans; } }
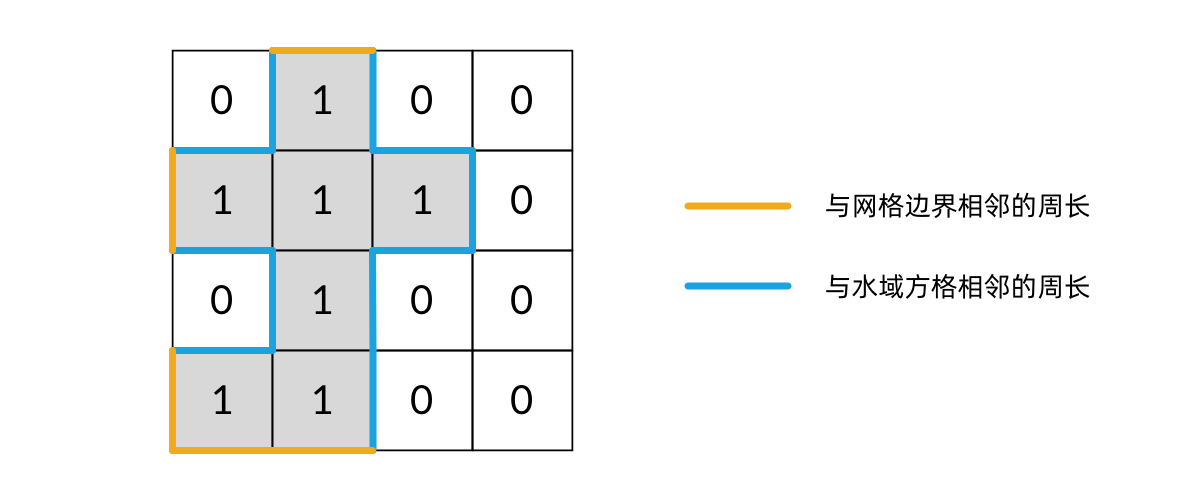
给定一个 row x col 的二维网格地图 grid ,其中:grid[i][j] = 1 表示陆地, grid[i][j] = 0 表示水域。
网格中的格子 水平和垂直 方向相连(对角线方向不相连)。整个网格被水完全包围,但其中恰好有一个岛屿(或者说,一个或多个表示陆地的格子相连组成的岛屿)。
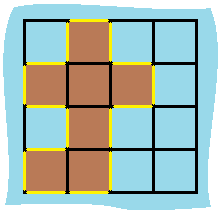
岛屿中没有“湖”(“湖” 指水域在岛屿内部且不和岛屿周围的水相连)。格子是边长为 1 的正方形。网格为长方形,且宽度和高度均不超过 100 。计算这个岛屿的周长。
1 2 3 输入:grid = [[0,1,0,0],[1,1,1,0],[0,1,0,0],[1,1,0,0]] 输出:16 解释:它的周长是上面图片中的 16 个黄色的边
思路:DFS 求岛屿的周长其实有很多种方法,如果用 DFS 遍历来求的话,有一种很简单的思路:岛屿的周长就是岛屿方格和非岛屿方格相邻的边的数量。注意,这里的非岛屿方格,既包括水域方格,也包括网格的边界。我们可以画一张图,看得更清晰:
将这个“相邻关系”对应到 DFS 遍历中,就是:每当在 DFS 遍历中,从一个岛屿方格走向一个非岛屿方格,就将周长加 1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class Solution { public int islandPerimeter (int [][] grid) { for (int r = 0 ; r < grid.length; r++) { for (int c = 0 ; c < grid[0 ].length; c++) { if (grid[r][c] == 1 ) { return dfs(grid, r, c); } } } return 0 ; } int dfs (int [][] grid, int r, int c) { if (!(0 <= r && r < grid.length && 0 <= c && c < grid[0 ].length)) { return 1 ; } if (grid[r][c] == 0 ) { return 1 ; } if (grid[r][c] != 1 ) { return 0 ; } grid[r][c] = 2 ; return dfs(grid, r - 1 , c) + dfs(grid, r + 1 , c) + dfs(grid, r, c - 1 ) + dfs(grid, r, c + 1 ); } }
如果我们可以将小写字母插入模式串 pattern 得到待查询项 query,那么待查询项与给定模式串匹配。(我们可以在任何位置插入每个字符,也可以插入 0 个字符。)
给定待查询列表 queries,和模式串 pattern,返回由布尔值组成的答案列表 answer。只有在待查项 queries[i] 与模式串 pattern 匹配时, answer[i] 才为 true,否则为 false。
1 2 3 4 5 6 输入:queries = ["FooBar","FooBarTest","FootBall","FrameBuffer","ForceFeedBack"], pattern = "FB" 输出:[true,false,true,true,false] 示例: "FooBar" 可以这样生成:"F" + "oo" + "B" + "ar"。 "FootBall" 可以这样生成:"F" + "oot" + "B" + "all". "FrameBuffer" 可以这样生成:"F" + "rame" + "B" + "uffer".
思路:字符串匹配 我们依次取出quries数组中需要查询的每个字符串,将它和pattrn进行匹配,并将每次匹配的结果加入结果数组中。
算法:
对于一个带查询的字符串query和pattrn我们可以用如下的方式判断它们是否匹配
开始分别用两个指针idx1和idx2指向query和pattrn的头部。
判断两个指针所指向的字符是否相等,如果相等则同时后移
若不相等,则idx1的指针不断后移,直到走到query字符串末尾或和idx2指向的字符相等。注意根据题意我们只能插入小写字母,故idx1后移的过程中若遇到不匹配大写字母,则立即返回false。
当指针idx1或idx2走到字符串的末尾时退出循环,这时我们要判断idx2是否走到了pattrn字符串的末尾,如果不是,说明我们还有剩余字符未成功匹配,返回false。同时我也要判断query中剩余的字符中是否全是小写字母,若不是返回false。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class Solution { public List<Boolean> camelMatch (String[] queries, String pattern) { List<Boolean> ans = new ArrayList <>(); for (String query : queries){ ans.add(isMatch(query,pattern)); } return ans; } private Boolean isMatch (String query,String pattern) { int idx1 = 0 , idx2 = 0 , n1 = query.length(),n2 = pattern.length(); while (idx1 < n1 && idx2 < n2){ char ch1 = query.charAt(idx1),ch2 = pattern.charAt(idx2); if (ch1 == ch2){ idx1++; idx2++; }else { if (ch1 >= 'A' && ch1 <= 'Z' ) return false ; idx1++; } } if (idx2 != n2 ) return false ; while (idx1 < n1){ char ch1 = query.charAt(idx1++); if (ch1 >= 'A' && ch1 <= 'Z' ) return false ; } return true ; } }
设quries数组长度为N,字符串总长度为M,pattren的长度为K:
时间复杂度:O(M+N∗K)
空间复杂度:O(1) 不包含返回值数组所占用空间
以数组 intervals 表示若干个区间的集合,其中单个区间为 intervals[i] = [starti, endi] 。请你合并所有重叠的区间,并返回 一个不重叠的区间数组,该数组需恰好覆盖输入中的所有区间 。
1 2 3 输入:intervals = [[1,3],[2,6],[8,10],[15,18]] 输出:[[1,6],[8,10],[15,18]] 解释:区间 [1,3] 和 [2,6] 重叠, 将它们合并为 [1,6].
思路:排序 我们用数组 merged 存储最终的答案。
首先,我们将列表中的区间按照左端点升序排序。然后我们将第一个区间加入 merged 数组中,并按顺序依次考虑之后的每个区间:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution { public int [][] merge(int [][] intervals) { if (intervals.length == 0 ){ return new int [0 ][2 ]; } Arrays.sort(intervals,new Comparator <int []>(){ public int compare (int [] interval1 , int [] interval2) { return interval1[0 ] - interval2[0 ]; } }); List<int []> merged = new ArrayList <int []>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < intervals.length; i++){ int L = intervals[i][0 ] , R = intervals[i][1 ]; if (merged.size()==0 || merged.get(merged.size() - 1 )[1 ] < L){ merged.add(new int []{L,R}); }else { merged.get(merged.size()-1 )[1 ] = Math.max(merged.get(merged.size()-1 )[1 ] ,R); } } return merged.toArray(new int [merged.size()][]); } }
时间复杂度:O(nlogn),n为区间的数量
空间复杂度:O(nlogn)
给你一个整数数组 nums ,请你找出数组中乘积最大的非空连续子数组(该子数组中至少包含一个数字),并返回该子数组所对应的乘积。
测试用例的答案是一个 32-位 整数。
子数组 是数组的连续子序列。
1 2 3 输入: nums = [2,3,-2,4] 输出: 6 解释: 子数组 [2,3] 有最大乘积 6。
思路:动态规划 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 class Solution { public int maxProduct (int [] nums) { int maxF = nums[0 ],minF = nums[0 ],ans = nums[0 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i < nums.length ; i++){ int mx = maxF , mn = minF; maxF = Math.max(mx*nums[i],Math.max(nums[i],mn*nums[i])); minF = Math.min(mn*nums[i],Math.min(nums[i],mx*nums[i])); ans = Math.max(maxF,ans); } return ans; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution { public int maxProduct (int [] nums) { int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE,imax =1 , imin = 1 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length ; i++){ if (nums[i] < 0 ){ int temp = imax; imax = imin; imin = temp; } imax = Math.max(imax * nums[i],nums[i]); imin = Math.min(imin * nums[i],nums[i]); max = Math.max(max , imax); } return max; } }
图解方法,非常易懂
把符合下列属性的数组 arr 称为 山脉数组 :
arr.length >= 3
思路:双指针(动态规划) 枚举山脚的方式:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 class Solution { public int longestMountain (int [] arr) { int ans = 0 , l = 0 , n = arr.length; while (l < n-1 ){ while (l<n-1 && arr[l] >= arr[l+1 ]){ l++; } int r = l ; while (r < n-1 && arr[r] < arr[r+1 ]){ r++; } int mid = r; if (r < n-1 && arr[r] > arr[r+1 ] ){ while (r < n-1 && arr[r] > arr[r+1 ]){ r++; } if (l!=mid && r != mid){ ans = Math.max(ans,r-l+1 ); } } l = r; } return ans; } }
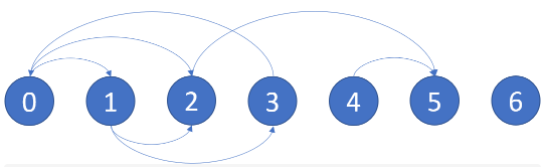
有一个有 n 个节点的有向图,节点按 0 到 n - 1 编号。图由一个 索引从 0 开始 的 2D 整数数组 graph表示, graph[i]是与节点 i 相邻的节点的整数数组,这意味着从节点 i 到 graph[i]中的每个节点都有一条边。
如果一个节点没有连出的有向边,则它是 终端节点 。如果没有出边,则节点为终端节点。如果从该节点开始的所有可能路径都通向 终端节点 ,则该节点为 安全节点 。
返回一个由图中所有 安全节点 组成的数组作为答案。答案数组中的元素应当按 升序 排列。
输入:graph = [[1,2],[2,3],[5],[0],[5],[],[]]
思路:拓扑排序 题目理解:对于一个起始节点,如果从该节点出发,无论每一步选择沿哪条有向边行走,最后必然在有限步内到达终点,则将该起始节点称作是安全的。
也就是说,对于某一个节点,如果它当前在某个环内,或者有可能走到某个环上,那么它就是不安全的,因为如果遇到环,就无法在有限步内到达终点。
结合上面的图例:
其中输入的graph数组中的元素代表了各点的指向情况,例如第一个元素[1,2]就表示以节点0为起点的边有两条,分别指向节点1和节点2。输出为[2,4,5,6],首先图中节点5和6都是出度为 0 的节点,他们本身就是终点,而2和4的情况相同,他们的出度都为 1,且都指向节点5,所以他们只能通过这条边走向终点5。
具体详解:拓扑排序
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 class Solution { public List<Integer> eventualSafeNodes (int [][] graph) { int n = graph.length; List<List<Integer>> new_graph = new ArrayList <List<Integer>>(); int [] Indeg = new int [n]; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { new_graph.add(new ArrayList <Integer>()); } for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < graph[i].length; j++) { new_graph.get(graph[i][j]).add(i); } Indeg[i] = graph[i].length; } Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList <Integer>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { if (Indeg[i] == 0 ) { q.offer(i); } } while (!q.isEmpty()) { int cur = q.poll(); for (int x : new_graph.get(cur)) { Indeg[x]--; if (Indeg[x] == 0 ) q.offer(x); } } List<Integer> ret = new ArrayList <Integer>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { if (Indeg[i] == 0 ) ret.add(i); } return ret; } }
给你链表的头节点 head 和一个整数 k 。
交换 链表正数第 k 个节点和倒数第 k 个节点的值后,返回链表的头节点(链表 从 1 开始索引 )
1 2 输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2 输出:[1,4,3,2,5]
思路:值交换 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution { public ListNode swapNodes (ListNode head, int k) { ListNode left = head; ListNode right = head; for (int i = 1 ; i < k; i++){left = left.next;} ListNode cur = left; while (cur.next != null ){ right = right.next; cur = cur.next; } int m = right.val; right.val = left.val; left.val = m; return head; } }
给你一个整数数组 nums,返回 nums 中最长等差子序列的长度。
回想一下,nums 的子序列是一个列表 nums[i1], nums[i2], …, nums[ik] ,且 0 <= i1 < i2 < … < ik <= nums.length - 1。并且如果 seq[i+1] - seq[i]( 0 <= i < seq.length - 1) 的值都相同,那么序列 seq 是等差的。
1 2 3 4 输入:nums = [3,6,9,12] 输出:4 解释: 整个数组是公差为 3 的等差数列
思路:动态规划 详解
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution { public int longestArithSeqLength (int [] nums) { int n=nums.length; int [][] dp=new int [n][1001 ]; int maxLen=0 ; for (int k=1 ;k<n;k++){ for (int j=0 ;j<k;j++){ int d=nums[k]-nums[j]+500 ; dp[k][d]=dp[j][d]+1 ; maxLen=Math.max(maxLen,dp[k][d]); } } return maxLen+1 ; } }
请你设计并实现一个满足 LRU (最近最少使用) 缓存 约束的数据结构。
思路:双向哈希链表 主要问题:为什么要用双向链表?如何更新新访问的值
详细思路
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 class LRUCache { int cap; LinkedHashMap<Integer, Integer> cache = new LinkedHashMap <>(); public LRUCache (int capacity) { this .cap = capacity; } public int get (int key) { if (!cache.containsKey(key)) { return -1 ; } makeRecently(key); return cache.get(key); } public void put (int key, int val) { if (cache.containsKey(key)) { cache.put(key, val); makeRecently(key); return ; } if (cache.size() >= this .cap) { int oldestKey = cache.keySet().iterator().next(); cache.remove(oldestKey); } cache.put(key, val); } private void makeRecently (int key) { int val = cache.get(key); cache.remove(key); cache.put(key, val); } }